How to Perform CNC Machining for Steel Parts
In precision parts machining factories with Swiss-type lathes as core equipment, CNC machining of steel parts requires balancing material characteristics and precision requirements. Steel, due to its high strength, wear resistance, and wide applicability, serves as a key material in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and other industries. The following details the core processes and technical key points of CNC machining for steel parts based on factory practices.
I. Material Characteristics and Equipment Selection
1. Difficulties in Steel Machining
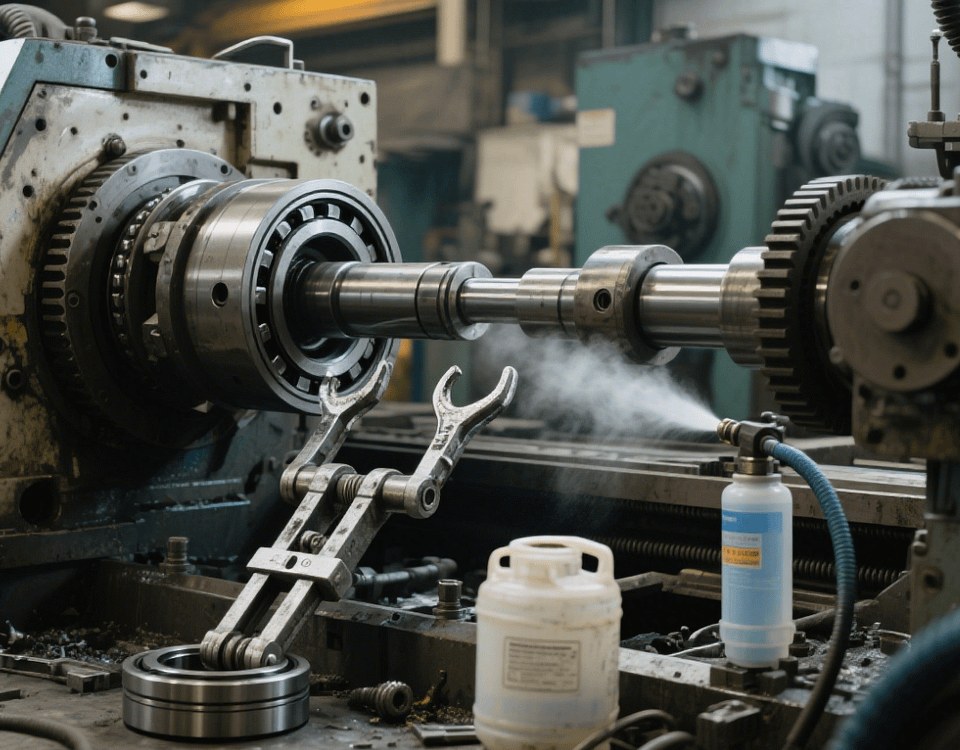
The high hardness (200-300HB) and poor thermal conductivity of steel (such as 45# steel and stainless steel 304) easily lead to intensified tool wear, increased cutting temperature, and even part thermal deformation during machining. For example, chips generated in stainless steel machining tend to adhere to tools, requiring special attention to cooling and chip removal.
2. Equipment and Tool Configuration
Advantages of Swiss-Type Lathes: High-precision five-axis Swiss-type lathes are selected to achieve one-clamping full-process machining of steel parts through high spindle speeds (10,000-30,000r/min) and multi-axis linkage functions, reducing positioning errors caused by multiple clampings.
Tool Selection: Ceramic or CBN (cubic boron nitride) coated tools are used, whose high temperature resistance (up to 1200℃) and wear resistance are 3-5 times higher than cemented carbide tools, suitable for high-speed cutting of steel.
II. Process Planning and Parameter Optimization
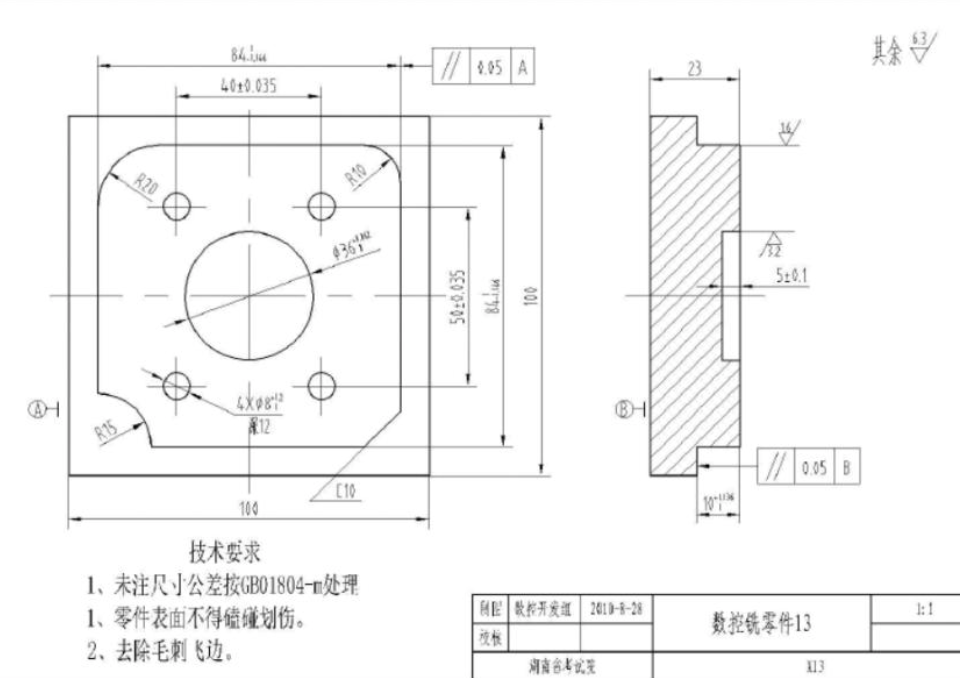
1. Drawing Analysis and Path Design
Taking steel shaft parts for automotive engines as an example, key focuses include:
Dimensional Accuracy: Diameter tolerance controlled within ±0.01mm, cylindricity ≤0.005mm;
Surface Requirements: Roughness Ra≤0.8μm, achieved through a three-stage process of rough turning – semi-finish turning – finish turning. CAM software is used to generate spiral interpolation paths to avoid tool edge chipping caused by right-angle cutting.
2. Cutting Parameter Optimization
In steel part machining, cutting parameters for different machining stages should be scientifically set:
Rough Machining Stage: Spindle speed controlled at 8,000-15,000r/min, feed rate 0.1-0.3mm/r, cutting depth 0.5-1.5mm, cooled by emulsion (concentration 8-10%).
Finish Machining Stage: Spindle speed increased to 15,000-25,000r/min, feed rate reduced to 0.05-0.1mm/r, cutting depth controlled at 0.05-0.2mm, cooling method using minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) with nitrogen.
III. Key Machining Technologies
1. Thermal Deformation Control
Layered Cutting: Control single cutting depth within 0.5mm, dispersing cutting heat through multiple passes;
Low-Temperature Cooling: Use -20℃ low-temperature nitrogen to spray the tool contact area, reducing cutting temperature by 40% and avoiding quenching effects during 45# steel machining.
2. Chip Handling Solutions
For chip winding issues in stainless steel:
Tool Edge Design: Adopt a 30° rake angle + chip breaker groove structure to break chips into C-shapes;
Negative Pressure Chip Removal: Remove chips in a timely manner through an internal vacuum pump of the machine tool (suction force ≥8kPa) to prevent tool post blockage.
IV. Quality Inspection and Process Optimization
1. Multi-Dimensional Inspection
Hardness Testing: Use a Rockwell hardness tester (HRC) to ensure quenched hardness meets standards (e.g., 45# steel after quenching and tempering HRC28-32);
Geometric Tolerance: Coordinate measuring machine detects coaxiality (≤0.01mm) and straightness (≤0.003mm/m).
2. Process Iteration
If part roundness deviation is found in inspection, optimize by adjusting cutting parameters (such as reducing feed rate by 10%) or replacing coated tools (such as TiAlN instead of TiN).
In precision steel part machining, through the high-precision control of Swiss-type lathes, scientific matching of tools and parameters, and full-process quality control, mass production of steel parts with micron-level precision can be achieved. With more than 10 years of experience in steel part machining, our factory provides customers with one-stop solutions from process design to finished product delivery.