How to Dismantle a CNC Lathe
During equipment upgrading or relocation, standardized dismantling of CNC lathes is crucial to ensure the precision of secondary use. Improper operations may cause guide rail deformation (error exceeding ±0.02mm) or control system damage, increasing maintenance costs by over 50%. Based on our factory’s 10 years of equipment maintenance experience, the following details the standardized operation process from safety preparation to component disassembly.
I. Preparatory Work
1. Tool and Material List
* Special Tools: Torque wrench (accuracy ±3%), puller, hydraulic pin extractor;
* Protective Equipment: Cut-resistant gloves, safety goggles, non-slip shoes;
* Recording Materials: Label stickers, marker pens, part storage boxes.
2. Equipment Power-off and Data Backup
1. Power Disconnection: Turn off the main switch and hang a “No Closing” sign;
2. Data Backup: Export machine parameters (such as pitch compensation values) and processing programs via USB.
II. Modular Dismantling Steps
1. Dismantling Peripheral Accessories
* Cooling System: Loosen quick connectors, empty cutting fluid, and remove the water tank and pipes;
* Protective Devices: Remove fixing bolts of the protective cover and carefully take down the sheet metal shell.
2. Core Component Separation
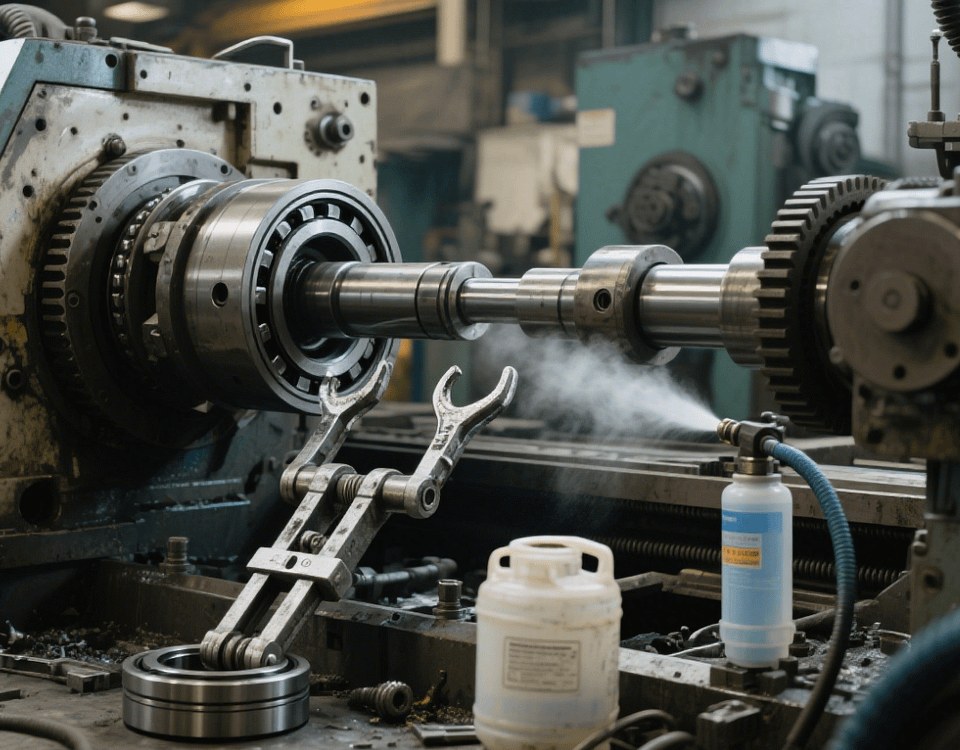
1. Turret Dismantling: Use a torque wrench to loosen fixing bolts, and two persons lift the turret synchronously;
2. Spindle Box Dismantling: Disconnect the belt and coupling, remove the bearing end cover, and extract the spindle with a puller;
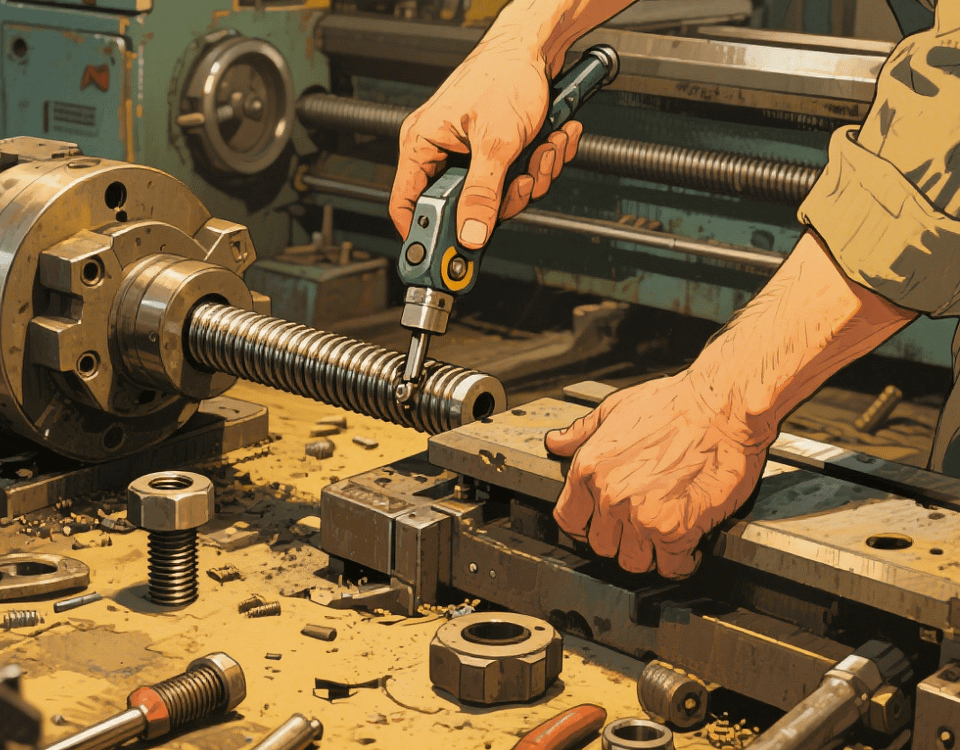
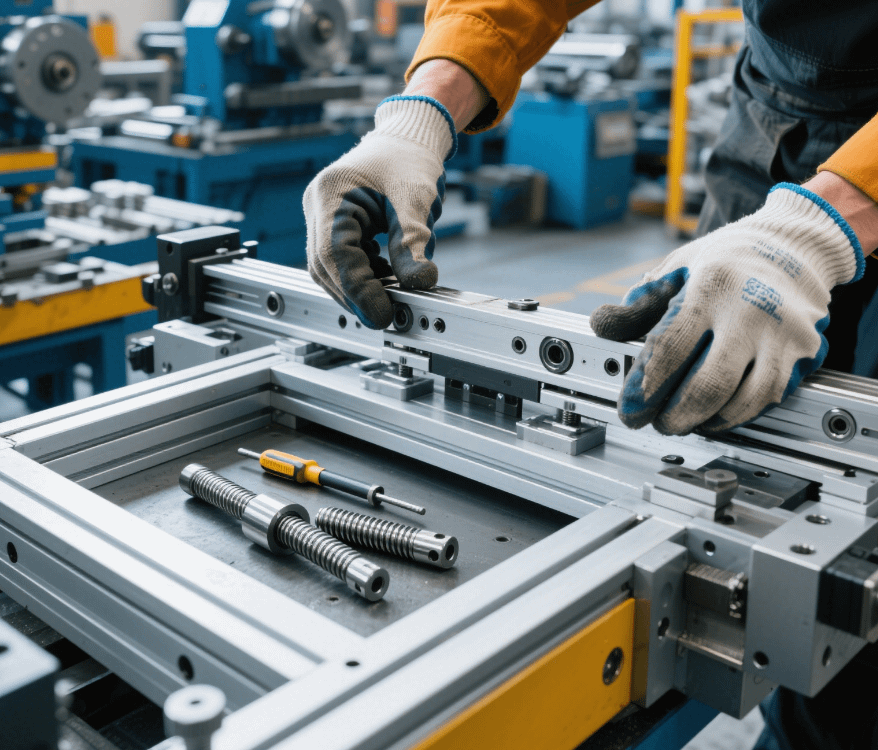
3. Ball Screw Dismantling: Loosen the nut seat, remove the positioning pin with a hydraulic pin extractor, and slowly pull out the screw along the axial direction.
3. Electrical System Handling
* Cable Marking: Label terminal numbers (e.g., X-axis servo motor cable) and take photos to record the wiring layout;
* Control Cabinet Dismantling: Disconnect circuit breakers, remove PLC modules and drivers, and pack them separately in anti-static bags.
III. Part Maintenance and Storage
1. Key Component Protection
* Guide Rail Rust Prevention: Apply lithium-based lubricating grease (thickness 0.1-0.2mm) and cover with plastic film;
* Screw Maintenance: Clean the thread surface, spray rust inhibitor, and wrap with oiled paper.
2. Classified Storage Management
Different component types have distinct storage requirements and applicable sample tools:
* Precision Parts: Require anti-vibration foam boxes + desiccants, with anti-static turnover boxes as sample tools;
* Large Components: Need horizontal placement + bracket support, with rubber pads as sample tools;
* Electrical Components: Should be stored in a moisture-proof cabinet (humidity ≤40%), with temperature and humidity recorders as sample tools.
IV. Relocation and Reinstallation Notes
1. Transportation Protection: Use air-ride vehicles for shock absorption and fix components to prevent shaking;
2. Installation Calibration: Re-calibrate the ball screw backlash with a laser interferometer (target value ≤0.003mm);
3. System Debugging: Restore backup parameters and run no-load for 30 minutes to detect operational status.
Standardized dismantling of CNC lathes should follow the principle of “from outside to inside, marking first”. Our factory is equipped with a professional equipment disassembly team, having completed the relocation and maintenance of over 50 imported CNC lathes. We provide full-process services from dismantling, transportation to installation and debugging, ensuring minimal precision loss and assisting enterprises in efficient equipment iteration.