Process Analysis of cnc machining partsby CNC Swiss-Type Lathe
CNC Swiss-type lathes have become a crucial part of the modern machining industry due to their flexibility and high-efficiency automation. They are excellent at handling complex, precise, small-batch, and variable parts machining tasks. When using a Swiss-type lathe forcnc machining parts, meticulous process analysis is the foundation for ensuring quality and efficiency.
1. Rational Selection of CNC Swiss-Type Lathe
When choosing a Swiss-type lathe, there are generally two scenarios. One is to select a suitable machine according to the part drawing and the blank. The other is to determine the appropriate parts to be machined on an existing lathe. In either case, factors such as the blank material, the complexity of the part contour, dimensions, machining accuracy, quantity of parts, and heat treatment requirements should be considered. The key is to meet cnc machining parts technical requirements, enhance productivity, and reduce production costs.
2. Processability Analysis of cnc machining parts by CNC Swiss-Type Lathe
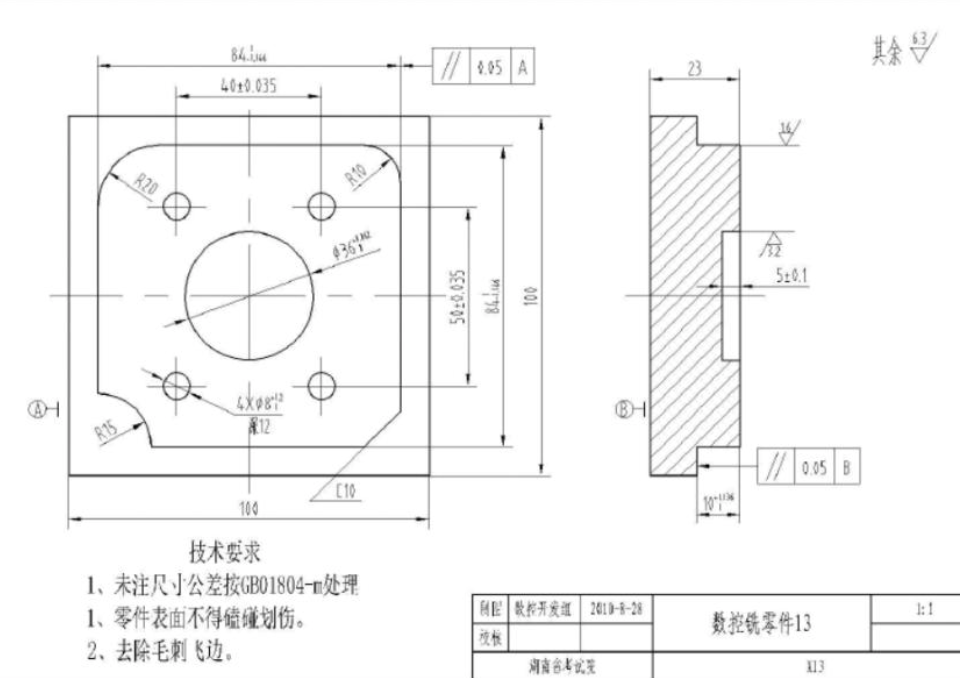
In terms of dimensioning on part drawings, it’s better to use the same datum for dimensioning or directly provide coordinate dimensions for easier programming. Also, the geometric elements of the part contour should have sufficient conditions to avoid programming difficulties.
For the structural processability, the inner cavity and outer shape of parts should preferably have a unified geometric type and size to reduce tool specifications and tool change times. A unified datum should be used for positioning. If there are no suitable positioning holes, process holes can be set.
3. Selection of Machining Methods and Determination of Machining Plans
The selection of machining methods should meet the requirements of machining accuracy and surface roughness, considering part shape, size, and heat treatment. For precise surface machining, it usually goes through roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing processes.
4. Division of Processes and Machining Steps
In CNC Swiss-type lathe machining, processes can be concentrated to complete most or all operations in one clamping. Machining steps should be divided considering accuracy and efficiency, like machining the same surface from rough to finish, or machining surfaces in the order of milling before boring.
5. Installation of cnc machining parts and Selection of Fixtures
During part installation, the design, process, and programming datums should be unified, and the number of clamping times should be minimized. When choosing fixtures, they should maintain a fixed coordinate direction relative to the machine and coordinate the size relationship between the part and the machine coordinate system.
6. Selection of Tools and Determination of Cutting Parameters
Tool selection affects machining efficiency and quality. Different tools are chosen according to machining tasks and part materials. Cutting parameters, including spindle speed, depth of cut, and feed rate, should be reasonably selected according to different machining methods.
7. Determination of Tool Setting Point and Tool Change Point
The tool setting point is the starting point of the tool’s movement relative to the part. It should be easy to locate and check. The tool change point should be set outside the part or fixture to avoid collisions.
8. Determination of Machining Route
The machining route should ensure part accuracy and surface quality, simplify numerical calculation, and be as short as possible. For point-to-point controlled Swiss-type lathes, the tool path should be planned to minimize the idle stroke.
In conclusion, mastering these aspects is essential for efficient and high-quality machining of mechanical parts using CNC Swiss-type lathes.