How to Set the Workpiece Zero Point on a CNC Machine
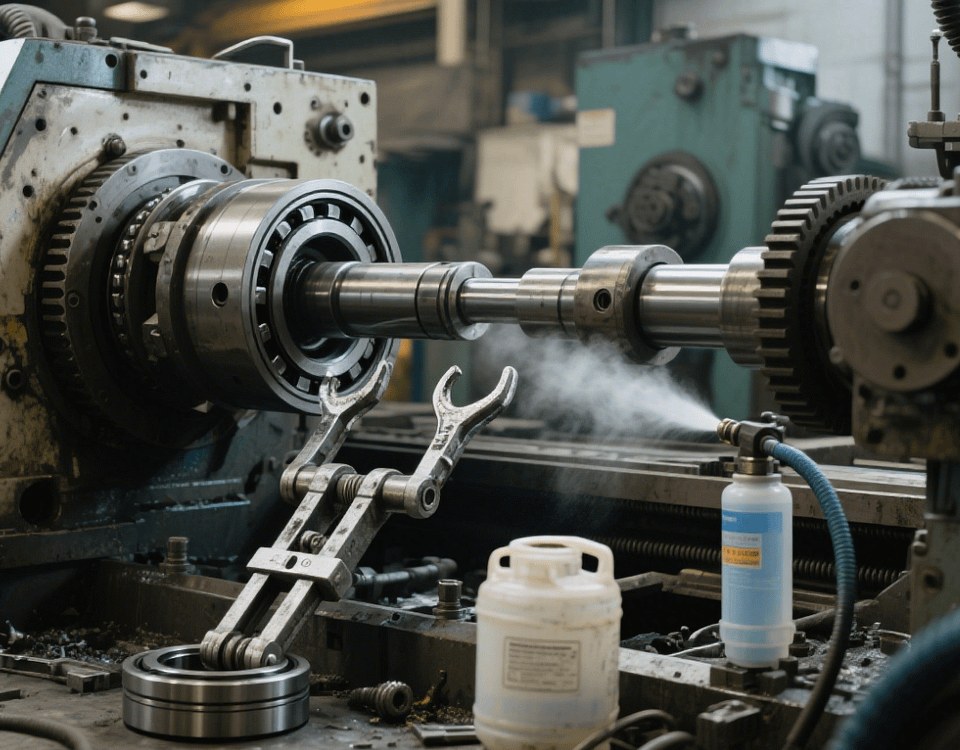
In our factory where we machine precision parts using Swiss-type lathes, heat is one of the key factors that affect the machining quality and performance of CNC parts. Whether it is the cutting heat generated during the machining process or the change in ambient temperature, it will have various effects on the parts. Understanding these effects and taking effective measures to deal with them is crucial for producing high-precision parts.
Firstly, heat can cause thermal deformation of the parts. During CNC machining, the friction between the tool and the workpiece, as well as the intense friction between the chips and the tool, will generate a large amount of heat. This heat will raise the local temperature of the workpiece, causing the material to expand. For precision parts, even the slightest dimensional change may cause the parts to exceed the tolerance range. For example, when machining thin-walled parts, excessive temperature may cause the thin-walled parts to twist and deform, seriously affecting the shape accuracy and assembly performance of the parts.
Secondly, heat can affect the surface quality of the parts. The cutting heat will change the physical and chemical properties of the surface material of the parts. High temperature may lead to phenomena such as oxidation and burning on the surface of the parts, reducing the surface finish. Moreover, heat may also cause changes in the metallographic structure of the surface layer, resulting in a decrease in material hardness or the generation of residual stress, affecting the wear resistance and fatigue strength of the parts. If the surface quality of the parts is not good, it will not only affect their appearance but also shorten the service life of the parts.
In addition, heat has a negative impact on the machining equipment. The heat generated when the machine tool operates under high load for a long time will cause thermal expansion of components such as the spindle and the guide rails of the machine tool, affecting its motion accuracy. The thermal deformation of the spindle may cause the rotation center of the tool to shift, reducing the dimensional accuracy of the machined parts; the thermal expansion of the guide rails will affect the linear motion accuracy of the worktable, causing machining errors. Once the accuracy of the machine tool decreases, it will be difficult to ensure the machining quality of the parts, and time and effort will be required for adjustment and maintenance.
In order to reduce the impact of heat on CNC parts, our factory has taken a variety of measures. For example, select appropriate cutting parameters, reduce the generation of cutting heat by reducing the cutting speed and feed rate; use efficient cutting fluid, which can not only take away a large amount of heat but also play a lubricating role and reduce friction; carry out reasonable cooling and thermal insulation design for the machine tool to control the temperature rise of the machine tool components. At the same time, we will also strictly control the ambient temperature of the workshop to create stable conditions for precision machining.
In the field of precision parts machining, fully understanding the influence of heat and effectively controlling it is an important link to ensure the quality of CNC parts. We will continue to optimize the machining process and equipment to ensure that each part can meet the high-standard quality requirements.