1:Determine the Actual Application Requirements of the Product
2:Transform the Application Requirements of Materials into Material Properties
01:Environmental Requirements
02:Technical Requirements
According to the technical requirements of the product, analyze the capabilities it needs to possess, which can cover a series of factors related to the application. For example: Does the product need to have the ability of conducting electricity, being insulated or being anti-static? Does it need heat dissipation, heat conduction or flame retardant properties? Does it need to come into contact with chemical solvents?
03:Physical Performance Requirements
Based on the intended use and usage environment of the product, analyze the physical properties required by the parts. For example: For parts that bear high stress or wear, factors such as strength, toughness and wear resistance are crucial; for parts that are exposed to high temperatures for a long time, good thermal stability is required.
04:Appearance and Surface Treatment Requirements
The market acceptance of a product depends to a large extent on its appearance. Different materials have different choices of color and transparency, as well as different smoothness and corresponding surface treatment methods. Therefore, the machining materials should be selected according to the aesthetic requirements of the product.
05:Machinability Considerations
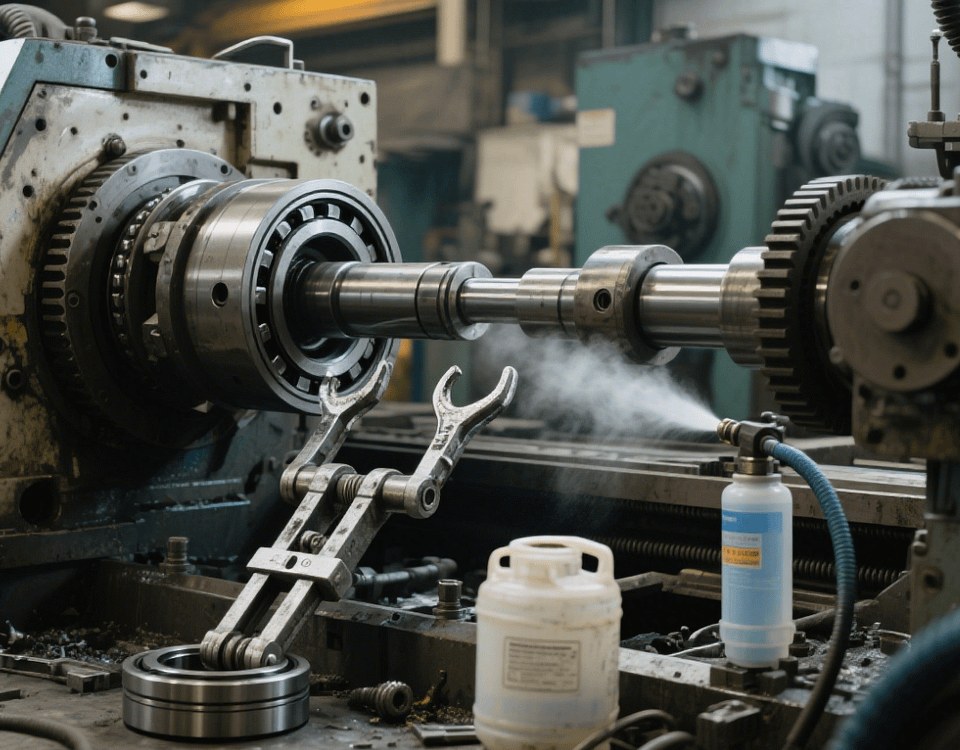
The machinability of materials will affect the manufacturing process and precision of parts. For example, although stainless steel is rust-proof and corrosion-resistant, it has high hardness and is prone to wearing out cutting tools during the machining process, resulting in very high machining costs and belonging to materials that are difficult to machine. While plastics have low hardness, they are prone to softening and deformation during the heating process and have poor stability. Selection should be made according to actual needs.
3:Look for Materials that Meet the Properties
Since the actual application requirements of a product are composed of multiple aspects, there may be cases where multiple materials meet the application requirements of one product, or the optimal choices for different application requirements correspond to different materials. Eventually, we may obtain several materials that meet the property requirements. Therefore, once the properties of the required materials are clearly defined, the remaining selection step is to research and seek the materials that best meet those properties.
The selection of candidate materials starts from consulting materials performance information. Of course, it is impossible and unnecessary to investigate thousands of application materials. We can start from the major categories of materials and first decide whether metal materials, non-metal materials or composite materials are needed. Then, based on the previous analysis results and corresponding to the material properties, narrow down the selection range of candidate materials. Finally, taking into account the material cost information, select the most suitable materials for the product from multiple candidate materials.